Anti-BullyingCollaborative Problem Solving | This week we will spend time on the topic of behavior management and strategies for anti-bullying. Here are a number of resources to explore and consider implementing in your work with children. Share your thinking about your research. You may include your rethinking about behavior, ideas for "Anthony", and strategies that you may want to trial in your new placement. Site your resources. Your response should be 300-500 words and respond to at least 2 others. Consider This: A child's behavior is a symptom of a difficulty (an unmet expectation and a child with skill deficits) that manifests into a behavior. A teacher's role is to identify the unmet expectations (academic/behavior/social) and the skill deficits that the child needs to learn to meet the expectation. Once understood, the educator creates a new set of expectations that allow the student to succeed and learn. Top Ten Classroom Management Ideas and Resources The Center on the Social and Emotional Foundations for Early Learning (CSEFEL) is focused on promoting the social emotional development and school readiness of young children birth to age 5. NICHCY is pleased to focus this page in our Behavior Suite on these three elements: conducting behavioral assessments, developing behavior plans, and providing positive behavior supports. PBIS World is a website containing links to hundreds of interventions, supports, resources, and data collection tools, all of which are organized into the tier 1 through 3 framework. Teaching Ideas has a ton of practical ideas in managing behavior. National Website on bullying. Bully Prevention Curriculum a document of supportive ideas and lessons Positive Behavior Support Strategies a document of supportive ideas Massachusetts Official Anti-Bullying Website (Free Materials). Stop Bullying.gov is another site for resources and ideas. Teaching Tolerance has a wealth of information on this subject. Click on the links to travel to resources. Creating a Classroom that Promotes Positive Behavior Here are the Guiding Principles. Supportive School Discipline has many resources to think and respond. Try Safe Supportive Learning Link as well. Massachusetts created links to their website to provide additional resources and information, especially connected to bullying issues and emotional development. Positive Behavior Intervention and Supports Sites The Casey and Bella Anti-Bully Curriculum Schoolwide Positive Interventions Addressing the Needs of Students with Disabilities in the IEP and in School Bullying Prevention and Intervention Efforts - Massachusetts Response. Here is the Federal Government's Response to Bullying and Special Education. Collaborative Problem Solving (Lives in the Balance) and Think Kids are two organizations that believe 'kids do well if they can'. They believe that when a child can not do well it is not because 'they don't want to' but that they are missing skills (lagging skills). These 'lagging skills' make it difficult or impossible to meet the expectations (behavior, emotional, social academic) that are needed to be successful. They DO NOT believe it is just a matter of 'will' and that you need to make them 'want to'. It is our job to help develop those skills so kids can meet the expectations. Their program provides the adult (parents, teachers, clinicians) with the skills to work with children with lagging skills. Article: Kids Do Well If They Can Bullying is unwanted, aggressive behavior among school aged children that involves a real or perceived power imbalance. The behavior is repeated, or has the potential to be repeated, over time. Both kids who are bullied and who bully others may have serious, lasting problems. |
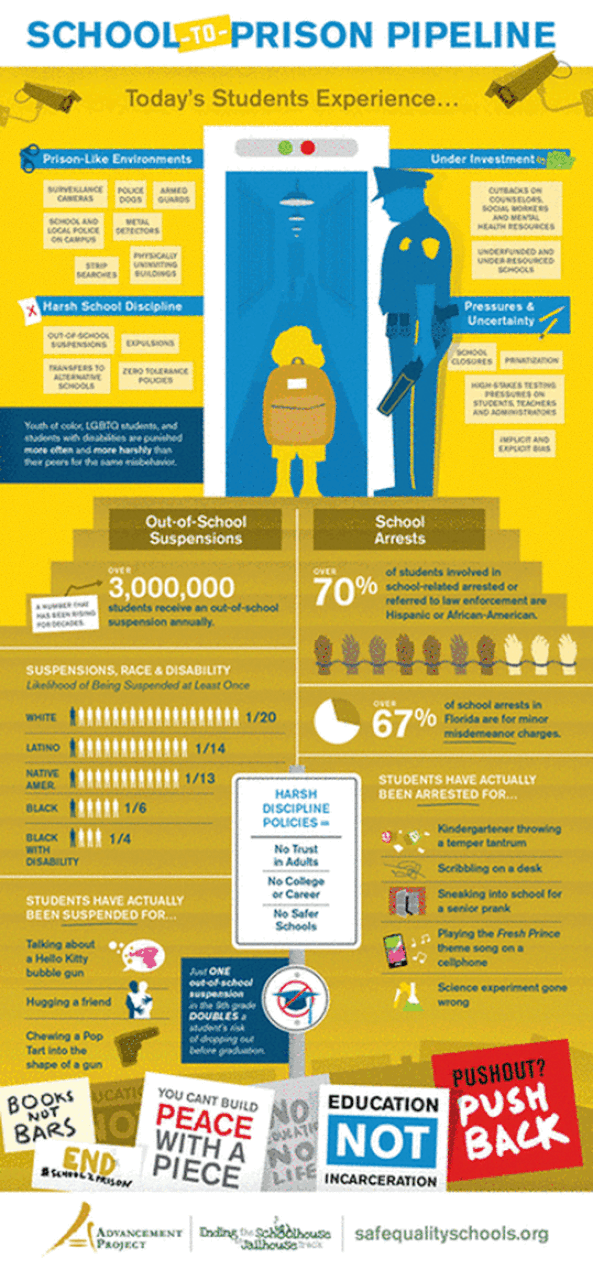
School to Prison Pipeline: When we fail to educate
Goal: Improve school discipline and school climate
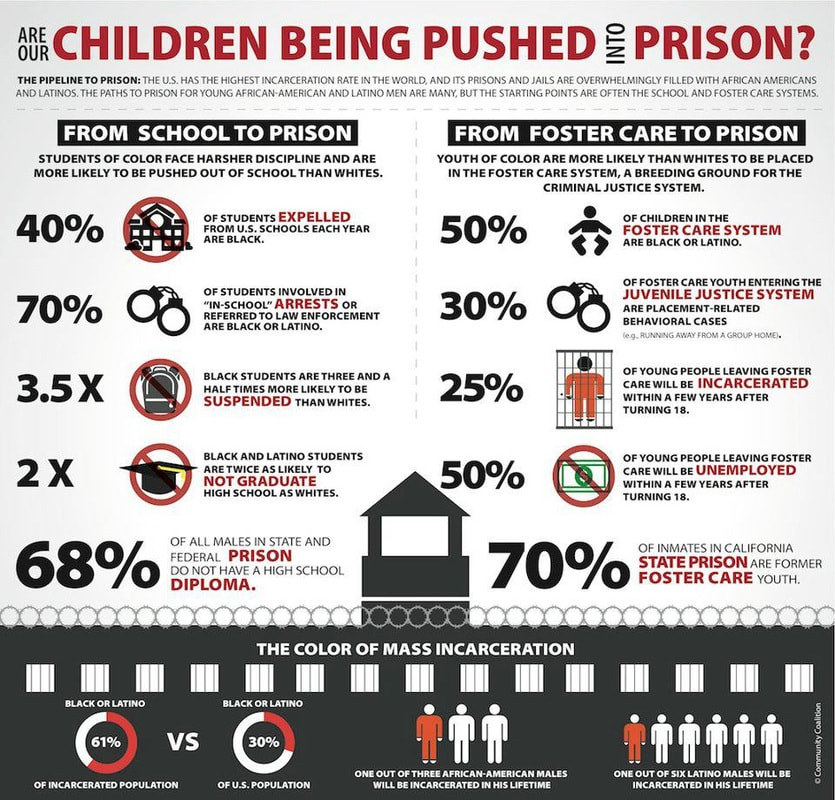
Reality: Kids with disabilities, especially minority kids, far more likely to be suspended, expelled, arrested, restrained than non-disabled kids.
Each year, significant numbers of students miss class due to suspensions and expulsions—even for minor infractions of school rules—and students of color and with disabilities are disproportionately impacted.
DOE and DOJ developed a package of guidance information that includes:
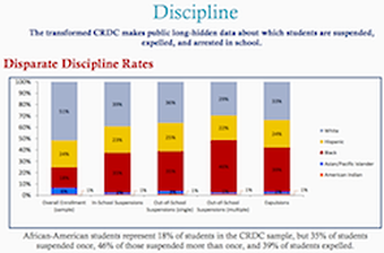
The transformed CRDC makes public long hidden data about discipline in schools. Get a good visual summary of all kinds of information about suspensions, expulsions, arrests, restraint and seclusion, student retention and… the disparate rates between disabled and non-disabled kids.
Reality: Kids with disabilities, especially minority kids, far more likely to be suspended, expelled, arrested, restrained than non-disabled kids.
Each year, significant numbers of students miss class due to suspensions and expulsions—even for minor infractions of school rules—and students of color and with disabilities are disproportionately impacted.
DOE and DOJ developed a package of guidance information that includes:
- Dear Colleague letter describing how schools can meet their legal obligations under federal law to administer student discipline without discriminating against students on the basis of race, color or national origin
- Publication about “best practices” describing three key principles and related action steps to guide state and local efforts to improve school climate and school discipline
- Directory of Federal School Climate and Discipline Resources
- Online Catalog of School Discipline Laws and Regulations
The transformed CRDC makes public long hidden data about discipline in schools. Get a good visual summary of all kinds of information about suspensions, expulsions, arrests, restraint and seclusion, student retention and… the disparate rates between disabled and non-disabled kids.
| | | | |

How we Misunderstand Incarceration
For Many With Disabilities, Special Education Leads To Jail (article)
Pipeline to Prison: Special education too often leads to jail for thousands of American children
Colorlines
Kids For Cash: Inside One of the Nation’s Most Shocking Juvenile Justice Scandals
Thousands of children in Pennsylvania were jailed by two corrupt judges who received $2.6 million in kickbacks from the builders and owners of private prison facilities.
Disparities in School Discipline Move Students of Color Toward Prison
The ACLU is committed to challenging the "school to prison pipeline," a disturbing national trend wherein children are funneled out of public schools and into the juvenile and criminal justice systems.
A $5 Children's Book vs. a $47,000 Jail Cell
The Prison Industry in the United States: Big Business or a New Form of Slavery?
Rerouting the Pipeline is a great article for educators to read.
Disability Rights Network and The Arc
These organizations speak about the disabled in the prison system.
neaToday The School to Prison Pipeline: Time to Shut it Down More Resource Links on this Topic
Autism in the Criminal Justice System A Story About Blade
SchooltoPrison.org provides a password-protected forum for impact litigators, direct services attorneys and other legal advocates across the nation to share ideas and strategies to challenge the push-out of children from schools and into the juvenile and criminal justice systems.
New Approaches to stop the Pipeline
The Dignity in Schools Campaign (DSC) challenges the systemic problem of pushout in our nation's schools and advocates for the human right of every child to a quality education and to be treated with dignity. The DSC unites parents, youth, educators and advocates in a campaign to promote local and national alternatives to a culture of zero-tolerance, punishment and removal.
In 2014, Boston reviewed its work with males in BPS
Opportunity and Equity: Enrollment and Outcomes of Black and Latino Males in Boston Public Schools_ (Executive Summary)
National Adult Literacy
The National Adult Literacy Survey reported that the percentage of prisoners in U.S. jails who tested at the two lowest levels of reading proficiency is 70% (2003).
For Many With Disabilities, Special Education Leads To Jail (article)
Pipeline to Prison: Special education too often leads to jail for thousands of American children
Colorlines
Kids For Cash: Inside One of the Nation’s Most Shocking Juvenile Justice Scandals
Thousands of children in Pennsylvania were jailed by two corrupt judges who received $2.6 million in kickbacks from the builders and owners of private prison facilities.
Disparities in School Discipline Move Students of Color Toward Prison
The ACLU is committed to challenging the "school to prison pipeline," a disturbing national trend wherein children are funneled out of public schools and into the juvenile and criminal justice systems.
A $5 Children's Book vs. a $47,000 Jail Cell
The Prison Industry in the United States: Big Business or a New Form of Slavery?
Rerouting the Pipeline is a great article for educators to read.
Disability Rights Network and The Arc
These organizations speak about the disabled in the prison system.
neaToday The School to Prison Pipeline: Time to Shut it Down More Resource Links on this Topic
Autism in the Criminal Justice System A Story About Blade
SchooltoPrison.org provides a password-protected forum for impact litigators, direct services attorneys and other legal advocates across the nation to share ideas and strategies to challenge the push-out of children from schools and into the juvenile and criminal justice systems.
New Approaches to stop the Pipeline
The Dignity in Schools Campaign (DSC) challenges the systemic problem of pushout in our nation's schools and advocates for the human right of every child to a quality education and to be treated with dignity. The DSC unites parents, youth, educators and advocates in a campaign to promote local and national alternatives to a culture of zero-tolerance, punishment and removal.
In 2014, Boston reviewed its work with males in BPS
Opportunity and Equity: Enrollment and Outcomes of Black and Latino Males in Boston Public Schools_ (Executive Summary)
National Adult Literacy
The National Adult Literacy Survey reported that the percentage of prisoners in U.S. jails who tested at the two lowest levels of reading proficiency is 70% (2003).
- The U.S. Department of Justice and the U.S. Department of Commerce estimates that 30 percent of federal inmates, 40 percent of state prison inmates, and 50 percent of persons on death row are high school dropouts (2003, 2007).
- Dr. Andrew Sum and his colleagues at Northeastern University found that young people who drop out of high school are 63% more likely to be incarcerated or otherwise institutionalized than their peers with four-year college degrees (2009).








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed