Hearing Impairment in children, according to the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), is an impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a child’s educational performance but is not included under the definition of ‘deafness'. When comparing to deafness, hearing impairment is a hearing loss less than 90 decibels while deafness is a hearing loss greater than 90 decibels. There are four subcategories of hearing loss; conductive, sensorineural, mixed and central.
Conductive hearing lossConductive hearing loss occurs when sound is not conducted efficiently through the outer ear canal to the eardrum and the tiny bones (ossicles) of the middle ear Conductive hearing loss usually involves a reduction in sound level or the ability to hear faint sounds. This type of hearing loss can often be corrected medically or surgically.
Some possible causes of conductive hearing loss:
|
Sensorineural hearing lossSensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) occurs when there is damage to the inner ear (cochlea), or to the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. Most of the time, SNHL cannot be medically or surgically corrected. This is the most common type of permanent hearing loss.
Some possible causes of SNHL:
|
Mixed and Central hearing lossSometimes a conductive hearing loss occurs in combination with a Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL). In other words, there may be damage in the outer or middle ear and in the inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve. When this occurs, the hearing loss is referred to as a mixed hearing loss.
|
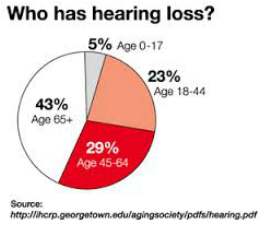
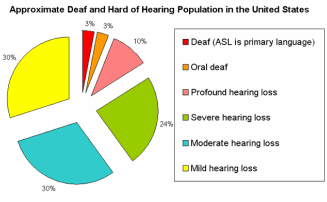
Statistics
|
Education and hearing loss
Having a hearing loss in a class is difficult and makes it hard to learn and participate at times. Some challenges that students face in class would be not understanding directions, not hearing the teacher, not able to pronounce words and sounds, etc. Not being able to produce words and sounds then makes it hard for them to read and spell. While these are common challenges for students with hearing loss or impairment, there are ways to help the students with the help of technology and other strategies.
|
In this video, there is a lot of information about hearing loss and strategies that students find helpful in the classroom. The information goes from what hearing loss is to what people use to help them hear from hearing aids to cochlear implants. In the second half of the video, the students who have hearing loss describe what it is like to have it and what they find helpful. Some helpful ideas they describe was having the teacher face them when they talk so they can read their lips, having the teacher repeat special announcements and instructions, and having a personal FM system so they can hear just the teacher in a loud area.
|
|
|
According to Special Education Guide, there are tips and strategies for parents and teachers to use with a student with hearing loss. One strategy they recommend is getting early intervention for the child so they are able to work on their sounds and pronunciation early. Another strategy for students is to have a scribe that will write down notes for the student when their is a lecture base lesson being taught. Other strategies that this website recommends is lip reading, sign language and assistive technology can compensate for issues which make listening to lectures and participating in class discussions challenging. |